Should you repair or replace an inefficient pump?
Weighing the factors involved in this decision involves considering the wider process and supply chain context. By Steed Webzell for Operations Engineer
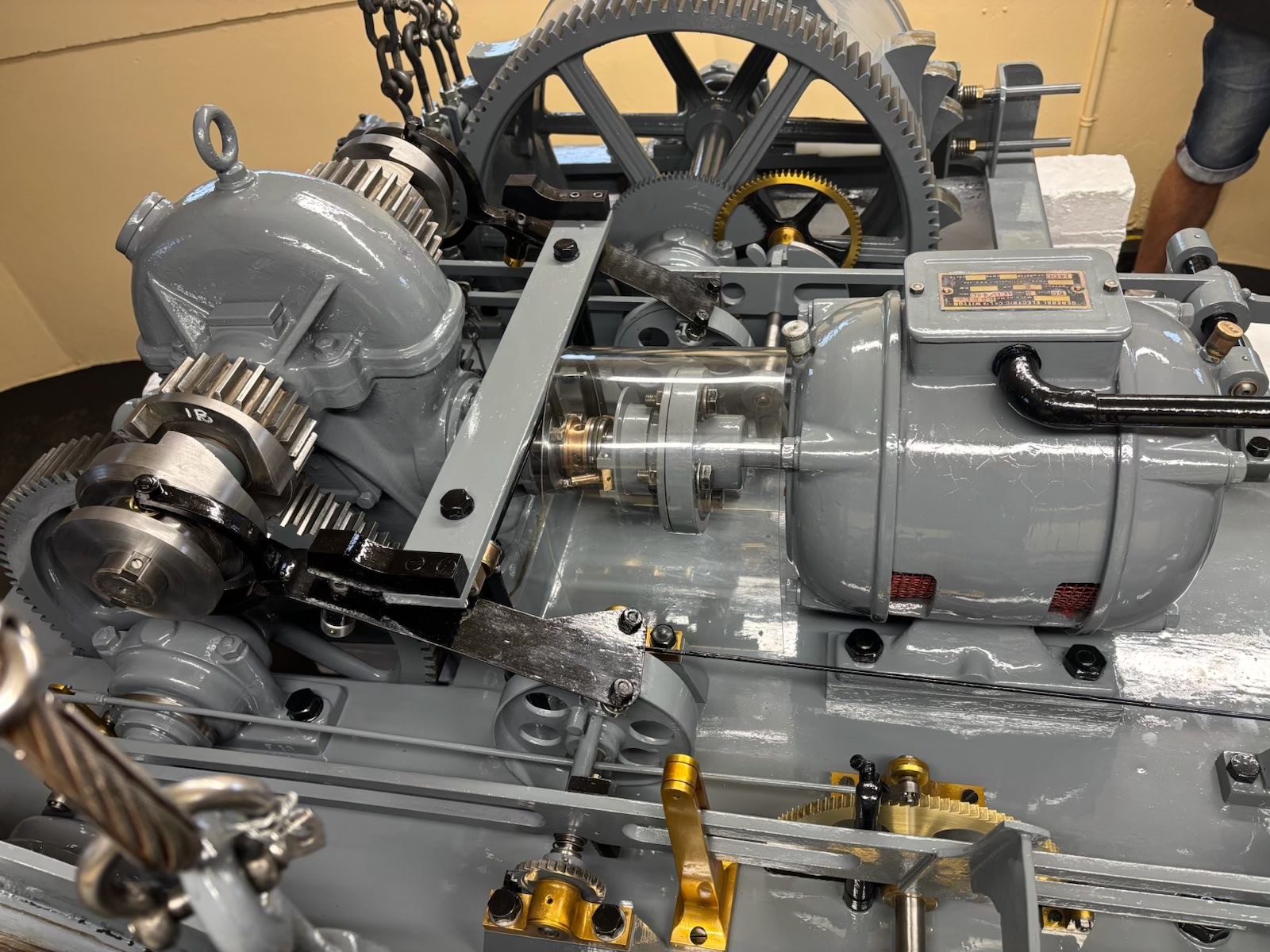
So, the pump is a little long in the tooth; it still functions but performance and efficiency have dipped to levels that are impacting operations and energy bills. Many plant engineers in this situation will have found themselves pondering the repair-or-replace dilemma.
Before determining the optimum way forward it is worth identifying why pump performance and efficiency diminish over time. According to Paul Pearce, sales director at industry service provider Rotamec Engineering Solutions, there are many factors at play here. He says: “Key influencers that affect pump performance include: surface roughness; internal clearances; mechanical losses such as bearing wear and failure; lip seal deterioration; mechanical seal deterioration; cavitation and impeller wear; and changes in the media being pumped.”
In the event that one or several of these circumstances begin to affect pump performance there will likely be a number of visual indicators, such as increased power consumption, reduced pressure or more frequent blockages. Further tell-tale signs can include increased vibration, higher operational noise levels, reduced production output, or the pump deviating from its performance curve.
PUMP MAINTENANCE
“The interval period for pump maintenance varies from application to application, but is typically determined by factors such as the media being pumped, the environment and the customer’s budget. To provide an example, we would recommend a service every six months for a sewage/wastewater pumping station, and generally an annual service/inspection on other pumped liquids,” explains Pearce.
For those thinking that a maintenance check comprises little more than a basic once-over, think again. At Rotamec, the company has a 19-point checklist of all pump components. Such checks include those for sump condition, motor resistance, cable condition and security, oil, impeller condition, vibration and noise, guide rail fixings, running amps, valves, earth bonding, and lifting chains.
“A standard pump repair at Rotamec would begin with a complete strip down and the identification of worn parts,” says Pearce. “A quotation is then provided for the required repair, including photographic evidence. Once approval is received, the repair is undertaken, with the pump re-assembled, tested, resprayed and despatched or reinstalled on site.”
PUMP REPLACEMENT
Of course, there are situations when a repair, no matter how effective, is not the way forward. For Rotamec, there are clear circumstances when this eventuality comes to bear.
“We would generally recommend pump replacement rather than repair and overhaul when the unit is either aged and parts are obsolete, when the power consumption on site dictates a pump upgrade, or when the repair/overhaul costs are more than 70% of a new replacement unit,” says Pearce. “However, as a matter of course, we always provide customers with a repair price [where possible] and a new unit price.”
Full article can be found here.